There are several different views on the definition. Some experts believe that it is more correct to use the general name - dorsalgia, or non-specific back pain. Difficulties in definition are also due to the fact that a number of specialists work with this disease - neurologists, orthopedists, neurosurgeons and general practitioners. Sometimes a person diagnosed with spinal osteochondrosis is referred to a cardiologist, since the manifestations of the disease are very similar to pain in the heart.
The term "osteochondrosis of the spine" was proposed by Hildebrandt in 1933 as a multifactorial degenerative disease of the spinal motion segment.
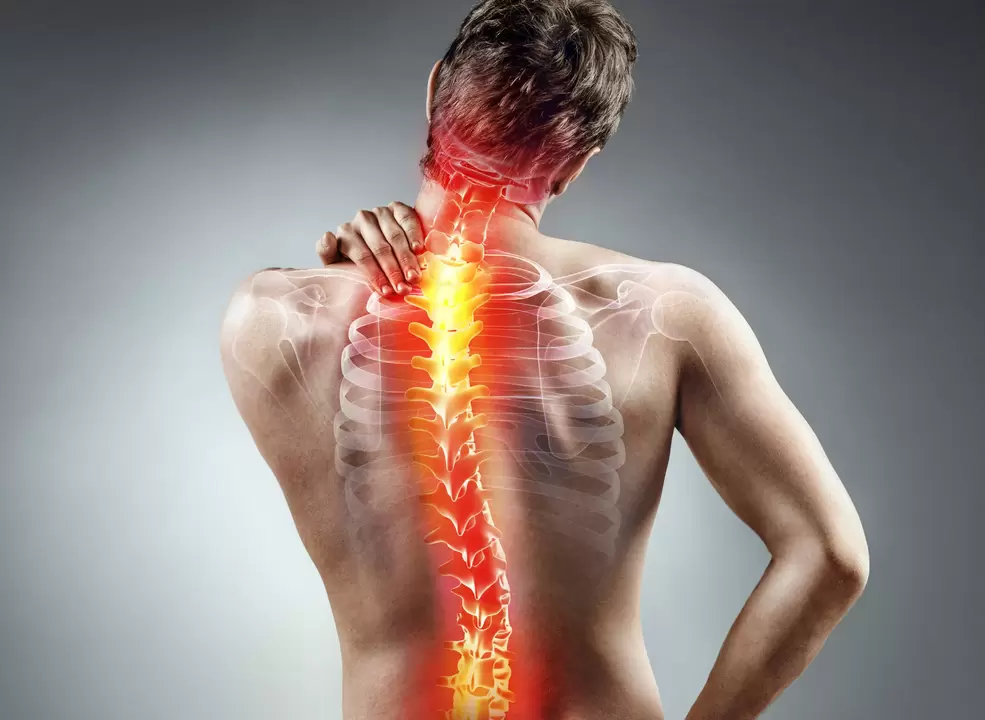
Spinal osteochondrosis is a pathological process in the spine characterized by degenerative-destructive disorders of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs. The risk of the disease is due to the hidden course of the process after admission, patients enter the stage of complications, when severe pain begins.
Causes of osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis of the spine appears as a result of the influence of predisposing factors on the human body. The disease does not differ according to gender. Causes for the development of osteochondrosis:
- inheritance;
- back injuries;
- congenital or acquired defects in the structure of the musculoskeletal system (flat feet, changes in posture);
- metabolic failures caused by diseases of internal secretion organs;
- poor nutrition and excess weight;
- viral and bacterial infections;
- lifestyle: lifting and holding heavy objects, working with electricity, constant exposure to vibrations, physical inactivity;
- constant psycho-emotional overload;
- bad habits: smoking, alcohol, opiates.
Osteochondrosis of the spine: types
Spinal osteochondrosis is divided according to the level of damage, each type has its own distinguishing features and features of treatment.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine.
The most common back disease is osteochondrosis of the lumbar region, which is associated with a large load on this particular region. Prone to complications such as intervertebral disc protrusion and the appearance of hernias, single and multiple. In case of complications, it can be associated with dysfunction of the pelvic organs and atrophy of the muscles of the lower extremities.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Second place in the classification of back diseases. Pathological processes develop as a result of a sedentary lifestyle and increased load on the shoulder girdle. Neck muscles require special training, in the absence of which they simply cannot cope with the load given their poor development.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
The rarest pathology of the back due to the low mobility of the region and the most developed muscular corset. It is difficult to diagnose due to a long asymptomatic course and imitation of other diseases (coronary artery disease, intercostal neuralgia, lung diseases).
Common process
The pathology covers several departments at the same time, occurs rarely and against the background of congenital diseases of the musculoskeletal system and is practically untreatable.
Stages of osteochondrosis and possible complications
A description of the four stages of spinal osteochondrosis was proposed by Osna in 1971. They are not used to formulate a diagnosis, but allow us to understand how the disease progresses.
- Intervertebral discs become less elastic. The disc may be slightly deformed, the internal nucleus pulposus is displaced within the disc. This stage is either not manifested at all, or small pains appear.
- In the second stage, cracks may appear in the disc and the surrounding ligaments weaken. The joint of the vertebrae becomes unstable. Attacks of acute pain with limited ability to work occur.
- The third stage is characterized by complete damage to the intervertebral disc. When the nucleus pulposus extends beyond the disc, an intervertebral disc herniation occurs. Spinal deformity or pinched nerve roots may occur.
- In the fourth stage, the surrounding tissues are affected - vertebrae, ligaments, spinal membranes. As a result, the spinal segment can completely lose mobility.
As a result of spinal osteochondrosis, various complications arise in some cases. Intervertebral disc problems, herniation and protrusion can lead to spinal canal narrowing, spinal cord compression and disability.
Depending on the level of damage, various problems with nerve root involvement are possible. It is about intercostal neuralgia, disorders of sensitivity and motor function of the upper and lower extremities, as well as disorders in the functioning of internal organs. Inflammation of the sciatic nerve, or sciatica, not only causes severe pain, but can also lead to pelvic disease and infertility.
In addition to nerve roots, osteochondrosis can cause compression of vertebral vessels. If blood flow is interrupted in the vertebral arteries, which flow in the cervical region and supply the brain, brain disorders, problems with vision or hearing, breathing or cardiac function may develop.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
In the framework of official medicine, the diagnosis of osteochondrosis includes an examination by a neurologist to determine the degree of nerve root damage, testing of reflexes and sensitivity.
The following instrumental methods can be used:
- Vascular ultrasound can reveal the degree of circulatory disturbance, for example, in the vertebral arteries;
- X-ray of the spine;
- CT also uses x-ray methods, but it allows you to create a three-dimensional image of the area being studied and detect even small displacements of the vertebrae;
- MRI specializes in the study of soft tissues, allows you to assess the condition of the spinal cord and visualize the internal structure of the intervertebral disc.
For differential diagnosis, laboratory tests, general blood and urine tests and calcium metabolism are used.
Therapy for osteochondrosis is complex.
- The first and very important drug in the treatment of osteochondrosis is lifestyle. Normalization of working conditions, moderate and regular exercise, as well as healthy sleep significantly improve the condition of patients.
- For the drug treatment of spinal osteochondrosis, a neurologist or a general practitioner can prescribe medications. Most often, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed - this is the standard treatment for spinal osteochondrosis. They reduce pain and reduce inflammation. Muscle relaxants help reduce muscle spasms. Vitamins and antioxidants are prescribed to protect nerve tissue from damage. However, every drug has side effects, for example, NSAIDs can negatively affect the stomach.
- In addition to medications, physiotherapy is also used, for example massage for osteochondrosis of the spine, as well as manual therapy. In case of severe complications of osteochondrosis, surgery may be required, but it is prescribed only if there is no effect from long-term conservative treatment.